Optimizing Kubuntu 24.04 LTS
Optimizing Kubuntu 24.04 LTS
Some useful links for optimizing system performance
Arch
KDE
Ubuntu
Ubuntu Desktop optimization
Ubuntu system hardening guide for desktops and servers
My Setup
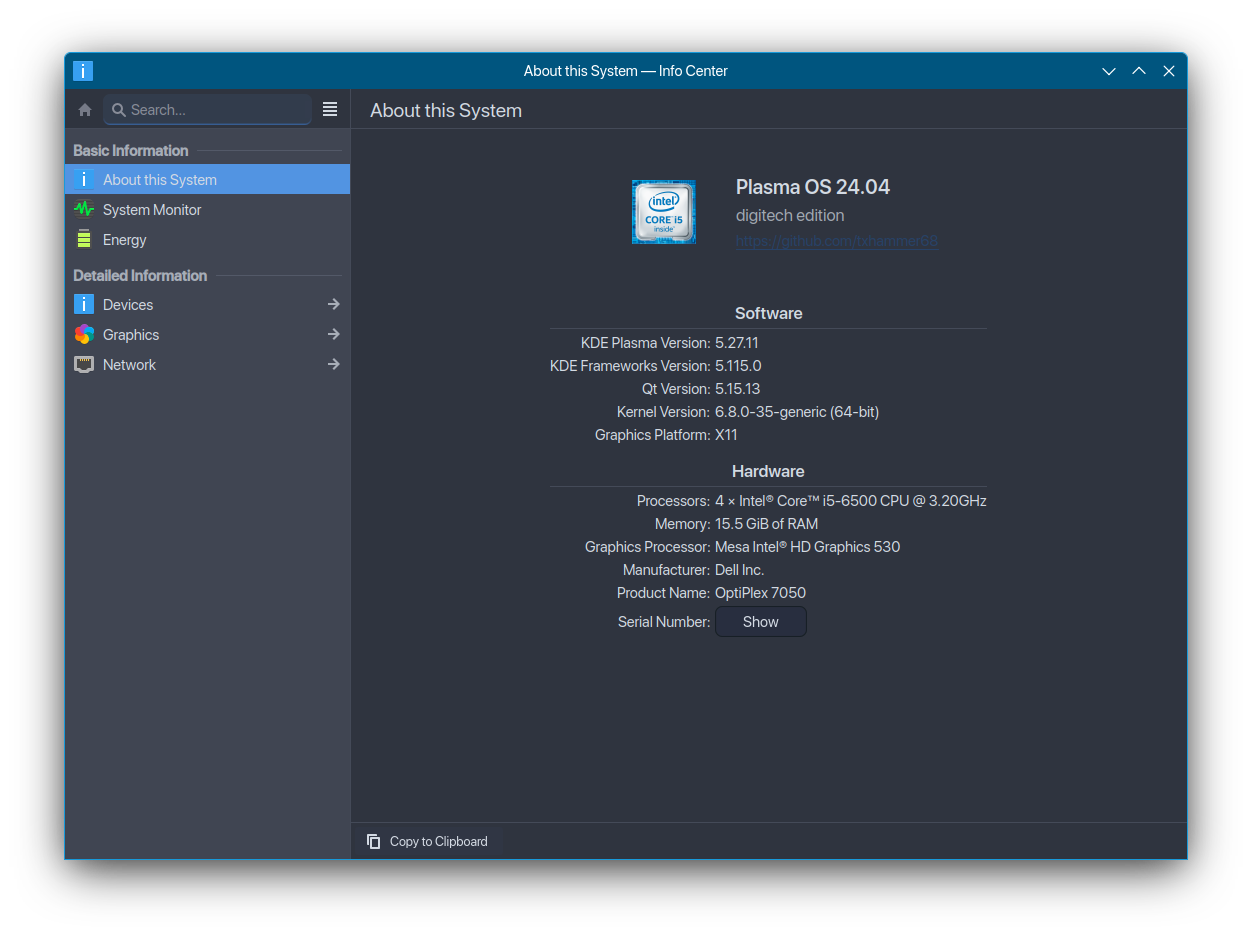
- Dell Optiplex 7050 Intel Core 5-Skylake CPU OC’d to 3.6Ghz 16GiB RAM, 500GiB NVME-SSD, 4TiB HDD
- Intel GPU 1920x1080 ,100Mib Internet
Caution, some settings are specific for my system setup, trying to get every performance gain i can on this older PC.
** USE At OWN RISK! **
Pre Install Setup
Create partitions for each drive before the install process
- EFI partition for UEFI Boot drive 512MiB type fat32 /dev/nvme0n1p1
- More space for custom kernel testing
- Root system partition remaining space type ext4 /dev/nvme0n1p2
- Swap space file 4GiB
- Data drive 4TiB hdd ext4 /dev/sdc1
Install as usual after creating partitions.
Reboot
System Tuning
Before making changes to your system run these commands and take note of the info, then compare when finished
Check system log for errors or issues, try to resolve those first before proceeding
free -m
sudo hdparm -t --direct /dev/nvme0n1p2
systemd-analyze critical-chain
systemd-analyze --user blame
fstab
The fstab file configures the mounted drives/partitions
Obtain UUID for each drive/partiton on system. ext4
lsblk -f
edit /etc/fstab
Root UUID="" / ext4 defaults,noatime,auto_da_alloc,inode_readahead_blks=64,errors=remount-ro 0 1
Data UUID="" /home/Data ext4 defaults,noatime,auto_da_alloc,inode_readahead_blks=64,errors=remount-ro 0 2
tmpfs /tmp tmpfs defaults,rw,nosuid,nodev,size=50%,noatime,nr_inodes=10k,mode=1777 0 0
/swapfile swap swap defaults,noatime 0 0
- noatime - disable access time stamps
- auto_da_alloc - If auto_da_alloc is enabled, ext4 will detect the replace via-rename and replace-via-truncate patterns and orce that any delayed allocation blocks are allocated such that at the next journal commit
- inode_readahead_blks - This tuning parameter controls the maximum number of inode table blocks that ext4’s inode table adahead algorithm will pre-read into the buffer cache. The value must be a power of 2. The default value is 32 blocks
EXT4 options
Enable fast_commit journal option speed up FS writes
sudo tune2fs -O fast_commit /dev/nvme0n1p2
sudo tune2fs -O fast_commit /dev/sdc1
Verify
sudo tune2fs -l /dev/nvme0n1p2 | grep features
Grub options
/etc/default/grub
- Turning off CPU exploit mitigations may improve performance.
ro quiet mitigations=off loglevel=3
CPUFreqUtils Change CPU Governor and Frequencies
/etc/init.d/cpufrequtils
ENABLE="true"
GOVERNOR="performance"
MAX_SPEED="3600000"
MIN_SPEED="2000000"
Intel GPU
i915 GPU settings edit /etc/modprobe.d/i915.conf
options i915 modeset=1 mitigations=off enable_fbc=1 enable_guc=2 enable_psr=0
- Override the security mitigations default for the Intel graphics driver for perfromance gains.
- Framebuffer compression (FBC) is a feature that can reduce power consumption and memory bandwidth during screen refreshes.
- GuC is designed to perform graphics workload scheduling on the various graphics parallel engines, (better.faster x264 decoding)
- Panel Self Refresh (PSR), a power saving feature used by Intel iGPUs is known to cause flickering in some instances.
- Some usefull tools for Intel GPU’s
sudo apt install intel-media-va-driver *(decode) intel-media-va-driver-non-free *(encode) firmware-misc-nonfree intel-gpu-toolsRun
sudo update-initramfs -uVerify changes after rebootsudo systool -m i915 -av
Additonal System Tuning
Sysctl Settings
Some useful sysctl settings edit /etc/sysctl.conf
kernel.sysrq=0
kernel.nmi_watchdog=0
kernel.printk = 3 3 1 7
fs.file-max=209708
fs.inotify.max_user_instances=2048
fs.inotify.max_user_watches=126166
vm.max_map_count = 262144
vm.swappiness = 1
# vm.dirty_ratio = 20
# vm.dirty_background_ratio = 5
vm.dirty_bytes = 536870912 # 512Mib
vm.dirty_background_bytes = 67108864 # 64Mib
# speed up usb transfers, can't have both ratio or bytes, this will sync usb transfers after ~ 64Mib transfers
vm.dirty_expire_centisecs = 1000
vm.dirty_writeback_centisecs = 500
vm.min_free_kbytes = 167772
vm.overcommit_ratio = 50
vm.overcommit_memory = 1
kernel.dmesg_restrict=0
# Harden BPF JIT compiler
net.core.bpf_jit_harden = 1
###
### NETWORK SECURITY ###
###
# Prevent SYN attack, enable SYNcookies (they will kick-in when the max_syn_backlog reached)
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_syn_retries = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_synack_retries = 2
net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 4096
net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 15
net.ipv4.tcp_sack = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_timestamps = 0
net.ipv4.icmp_echo_ignore_broadcasts = 1
# Disable packet forwarding
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.forwarding = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.forwarding = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.forwarding = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.forwarding = 0
# Enable IP spoofing protection
# Turn on source route verification
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 2
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 2
# Disable Redirect Acceptance
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.secure_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.secure_redirects = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_redirects = 0
# Disable Redirect Sending
net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.send_redirects = 0
# Disable IP source routing
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0
net.ipv4.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0
net.ipv6.conf.all.accept_source_route = 0
net.ipv6.conf.default.accept_source_route = 0
# Don't relay bootp
net.ipv4.conf.all.bootp_relay = 0
# net.ipv4.tcp_ecn=0 disabled 1 = To enable ECN for both incoming and outgoing connections 2=To enable ECN only when requested by incoming connections (the reasonably safe, kernel default):
# Disable proxy ARP
net.ipv4.conf.all.proxy_arp = 0
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_ignore = 1
net.ipv4.conf.all.arp_announce = 2
# Mitigate time-wait assassination hazards in TCP
net.ipv4.tcp_rfc1337 = 1
# Enable bad error message Protection
net.ipv4.icmp_ignore_bogus_error_responses = 1
# ipv4 Performance options
net.ipv4.tcp_fastopen=3
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time=60
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_intvl=15
net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_probes=4
net.core.default_qdisc=fq
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control=bbr
net.ipv4.tcp_window_scaling = 1
# net.ipv4.tcp_notsent_lowat = 32768
net.core.rmem_max = 8388608
net.core.wmem_max = 8388608
net.core.rmem_default = 8388608
net.core.wmem_default = 8388608
net.core.optmem_max = 40960
net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 4096 87380 8388608
net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 4096 65536 8388608
net.ipv4.udp_rmem_min = 8192
net.ipv4.udp_wmem_min = 8192
net.ipv4.tcp_slow_start_after_idle = 0
net.ipv4.tcp_mtu_probing = 1
# net.ipv4.tcp_low_latency=1
net.ipv4.tcp_adv_win_scale=1
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1
net.unix.max_dgram_qlen = 50
net.ipv4.tcp_no_metrics_save = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_moderate_rcvbuf = 1
net.ipv4.tcp_retries2 = 15
net.ipv4.tcp_retries1 = 3
## Reset network w/ new options
net.ipv4.route.flush = 1
net.ipv6.route.flush = 1
Modprobe various driver settings
Disable power saving for audio device, remove pop sounds
Audio Device - create /etc/modprobe.d/audio.conf
options snd_hda_intel power_save=0 power_save_controller=N
After creating these files run
sudo update-initramfs -u -k all
This wil update boot image to include the changes.
Reboot.
Disable some uneeded system services
Disable ModemManager If you do not have a mobile broadband interface.
sudo systemctl disable ModemManager.service
sudo systemctl mask ModemManager.service
fwupd is a daemon allowing you to update some devices’ firmware, including UEFI for several machines.
Remove fwupd from boot, newer hardware may want to leave this enabled for future updates…
sudo systemctl disable fwupd.service
sudo systemctl mask fwupd.service
GPU-Manager is software that creates a xorg.conf for you. So running this in every boot is just overkill. You only need to run this if you change your GPU.
sudo systemctl disable gpu-manager.service
sudo systemctl mask gpu-manager.service
Logical Volume Manager (LVM) is a device mapper framework that provides logical volume management.
Disable LVM
sudo systemctl disable lvm2-monitor.service
sudo systemctl mask lvm2-monitor.service
Disable Wait for Network online service, slows down boot
sudo systemctl disable NetworkManager-wait-online.service
sudo systemctl mask NetworkManager-wait-online.service
Disable Ubuntu News Updates, only used for ssh connections
sudo systemctl disable motd-news.timer
sudo systemctl mask motd-news.timer
sudo systemctl disable apt-news.service
sudo systemctl mask apt.news.service
Minimize logging
- journald logging
Change log retention and logging settings, check logs first for errors
/etc/systemd/journald.conf
MaxRetentionSec=3month MaxFileSec=1month MaxLevelStore=err MaxLevelSyslog=err MaxLevelKMsg=err MaxLevelConsole=err MaxLevelWall=emergDisable evbug logging
EVBUG is the driver for the Linux kernel input subsystem’s event debugging. Enabling the EVBUG driver (INPUT_EVBUG) will cause all input events to be logged to the system log… So all key presses, mouse movements, etc, will end up in the kernel log. That includes all key presses, so logging your passwords and other data to the kernel log. Practically a built-in kernel key logger. modprobe blacklist
Not sure why this enabled on kubuntu maybe they forgot to disable after testing…, safe to disable/etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf blacklist evbugAfter creating these files run
sudo update-initramfs -uThis wil update boot image to include the changes.
Reboot.Set fsck check interval
50 boot-ups or 1 month, change devices for your system
sudo tune2fs -c 50 -i 1m /dev/nvme0n1p2 sudo tune2fs -c 50 -i 1m /dev/sdb1MultiMedia
- Restricted Codecs
sudo apt install gstreamer1.0-libav gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-plugins-ugly gstreamer1.0-vaapi libk3b-extracodecs lame libavcodec-extra libavcodec-extra60 intel-media-va-driver-non-freeTo automatically switch audio device to newly connected devices, create this file:
Used for HTPC connected to HDTV, when switching monitor outputs
/etc/pipewire/pipewire-pulse.conf.d/switch-on-connect.conf (or ~/.config/pipewire/pipewire-pulse.conf.d/switch-on-connect.conf)override for pipewire-pulse.conf file
pulse.cmd = [ { cmd = "load-module" args = "module-always-sink" flags = [ ] } { cmd = "load-module" args = "module-switch-on-connect" } ]Better Pulse Audio Settings
/etc/pulse/daemon.conf
default-sample-format = float32le default-sample-rate = 48000 alternate-sample-rate = 44100 default-sample-channels = 2 default-channel-map = front-left,front-right default-fragments = 2 default-fragment-size-msec = 125 resample-method = soxr-vhq avoid-resampling = yes high-priority = yes nice-level = -11 realtime-scheduling = yes realtime-priority = 9 rlimit-rtprio = 9 daemonize = noNetworking
systemd-resolved
systemd-resolved provides a system-level DNS cache that can substantially improve performance for applications that do not cache their own DNS results. DNS queries and responses have traditionally been unencrypted, but more and more resolvers now support DNS over an encrypted TLS connection (DNS over TLS.) TLS can help ensure that no parties between the DNS server and the resolver can see or modify the DNS responses.
CTRL Blog
Linux Insider
Blog
Check Status
resolvectl status
Edit /etc/systemd/resolved.conf
Add, change DNS to your preferred DNS server
DNS=1.1.1.1
FallbackDNS=8.8.8.8
Domains=~.
DNSSEC=yes
DNSOverTLS=yes
Cache=yes
Change Network Manager
/etc/NetworkManager/NetworkManager.conf
[main]
dns=systemd-resolved
Change network manager dns in gui to 127.0.0.53
if working just restart after changes to resolved.conf file
systemctl restart systemd-resolved.service
systemctl restart NetworkManager.service
if not running then
systemctl enable systemd-resolved.service
systemctl start systemd-resolved.service
Verify Status
resolvectl status
Some useful sites to verify internet security connection
No firewall needed as most of us are behind an ISP router that has a built in firewall
Test your connection
IP Leak Test
Cloudfare Test
Optimize network MTU
The ping command will let you know if the packet was sent as more than one fragment with multiple header data attached.
ping -s 1472 -c1 espn.com
Retest changing packet size until 0% packet loss
NFS Shares
sudo apt install nfs-kernel-server
Create /etc/exports
/home/data/Movies/ 192.168.1.0/24(ro,sync,no_subtree_check,no_root_squash,all_squash)
sudo exportfs -ra
sudo systemctl restart nfs-server
mount share
sudo mount -t nfs -o resvport,ro 192.168.1.101:/home/data/Movies/ /home/matt/Temp/
sudo showmount -e
For iOS NFS path
192.168.1.101:/home/data/Movies/
Remove snapd
snap list
sudo systemctl disable snapd.service
sudo systemctl disable snapd.socket
sudo systemctl disable snapd.seeded.service
sudo snap remove firefox
sudo snap remove snap-store
sudo snap remove gtk-common-themes
sudo snap remove gnome-3-38-2004
sudo snap remove core18
sudo snap remove snapd-desktop-integration
sudo rm -rf /var/cache/snapd/
sudo apt autoremove --purge snapd
rm -rf ~/snap
Create /etc/apt/preferences.d/nosnap.pref
This file forbids snapd from ever being installed by APT.
Package: snapd
Pin: release a=*
Pin-Priority: -10
Install Firefox PPA
Firefox Extensions
- Youtube enhancer extension
- Origin Ad-Blocker
- Cookies
- Duck-Duck Go
- HLS D-L
Firefox Config options
- Firefox smooth scroll
- Arch Firefox
- Github
- FastFox
- BetterFox
KDE Plasma Fixes
- Reduce systemd timeouts for desktop installations, the system will not “hang” for 90 seconds and longer from time to time when logging out, rebooting or shutting down.
- Edit etc/systemd/system.conf.d/99-systemtimeout.conf
Change line
[Manager] DefaultTimeoutStopSec=15sEdit /etc/systemd/user.conf.d/99-usertimeout.conf
Change line[Manager] DefaultTimeoutStopSec=15s - Disable fast user switching
- Edit /usr/share/kubuntu-default-settings/kf5-settings/kdeglobals
[KDE Action Restrictions] switch_user=false start_new_session=falseX11 setup for dual monitors
Run xrandr to get inuput id’s
Create /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/10-monitor.confSection "Monitor" Identifier "HDMI-3" Option "Primary" "true" Option "Enable" "true" Option "PreferredMode" "1920x1080x60.0" Option "Broadcast RGB" "Full" EndSection Section "Monitor" Identifier "HDMI-1" Option "RightOf" "HDMI-3" Option "Primary" "false" Option "Disable" "true" Option "Enable" "false" Option "PreferredMode" "1920x1080x60.0" Option "Broadcast RGB" "Full" EndSectionThis will allow SDDM to show login prompt focused on primary screen.
After creating this file runsudo update-initramfs -u
WSL messes up Qt.openUrlExternally()
sudo mv /usr/share/applications/wslview.desktop /usr/share/applications/wslview.desktop.disabled
MSFT is starting to mess with my linux desktop :(
Disable Qt Logging, add to /etc/environment or .bashrc
QT_LOGGING_RULES="*.debug=false;qt*.debug=false;qt5.debug=false;*.warning=false;*.critical=false;qt.qpa.xcb.xcberror.warning=false;qt.qpa.xcb.xcberror.error=false;qt.qpa.xcb.warning=false;qt.qpa.xcb.error=false;qt.qpa.xcb=false"
Allow xmlrequest for loading json files
Add to /etc/environment or .bashrc
QML_XHR_ALLOW_FILE_READ="1"
kdebugdialog5 - kde debugging settings
Remove extra fonts, check Noto Sans/Serif extra language fonts, unnecessary for most cases
Run this after, clean font cache
fc-cache -f -v
- Reboot to apply changes
systemd-boot and Unified Kernel Images
- Replace grub, speeds up boot time, this is the future of Linux startup
- A Unified Kernel Image (UKI) is a combination of a UEFI boot stub program, a Linux kernel image, an initramfs, and further resources in a single UEFI PE file (device tree, cpu µcode, splash screen, secure boot sig/key, …). This file can either be directly invoked by the UEFI firmware or through a boot loader.
- systemd-boot loader - grub replacement
- UKI
- different script using kernel cmdline options
Install systemd-boot loader
sudo apt install systemd-boot systemd-ukify sudo bootctl install --path=/boot/efiCreate /boot/efi/loader/loader.conf
timeout 0 default ubuntu* auto-entries 1 console-mode max editor falseCreate /etc/kernel/install.conf
layout=uki uki_generator=ukify BOOT_ROOT=/boot/efiCreate /etc/kernel/uki.conf
Cmdline=@/etc/kernel/cmdline OSRelease=@/etc/os-release Splash=/boot/bootSplash.bmpedit /etc/kernel/cmdline
Check /etc/default/grub for boot options of your system, add them here to cmdlineroot=UUID=efc95b50-5747-4cae-999e-45c286ae0389 ro quiet cpufreq.default_governor=performance raid=noautodetect nowatchdog preempt=full threadirqs mitigations=off loglevel=3 rd.udev.log-priority=3 udev.log_priority=3 systemd.show_status=auto vt.global_cursor_default=0 i915.modeset=1 i915.enable_fbc=1 i915.enable_psr=0 i915.enable_guc=2 i915.mitigations=off ipv6.disable=1 8250.nr_uarts=0 - preempt=full A fully-preemptible kernel is most suitable for low-latency workloads - such as gaming, live-streaming, multimedia, etc.
- threadirqs - Improved interrupt handling, by distributing interrupts across multiple threads, the system can handle a higher volume of interrupts concurrently, potentially reducing latency and improving responsiveness.
- nowatchdog
After install and setup of systemd-boot run
sudo update-initramfs -u -k all
Verify
sudo bootctl
Reboot
- Verify systemd proper operation
- Select systemd-boot menu by pressing space bar during boot up
- If all seems ok proceed to remove Grub
Remove Grub
sudo apt purge --allow-remove-essential grub2-common grub-pc-bin grub-pc grub-gfxpayload-lists grub-efi-amd64-bin grub-efi-amd64-signed grub-common os-prober shim-signed
apt-get autoremove --purge
rm -rf /boot/grub/
rm -rf /boot/efi/EFI/ubuntu
- Make sure GRUB is not installed back
sudo apt-mark hold "grub*"Create /etc/apt/preferences.d/nogrub.pref
This file forbids grub from ever being installed by APT.Package: grub* Pin: release a=* Pin-Priority: -10 - You can also remove plymouth boot splash manager
sudo apt purge plymouth && sudo apt autoremove sudo rm -rf /usr/share/plymouthReboot to verify grub is no longer installed and systemd-boot is working
- systemd-boot bootSplash logo

System should now be running at optimal performance and security
Other Misc
- Nala is a Python-based frontend for apt package management.
- aria2 is a lightweight multi-protocol & multi-source command-line download utility.
- Jellyfin is an open source media solution that puts you in control of your media.
- bleachbit cleaner
- clamav virus scanner
- Arch Stateful firewall